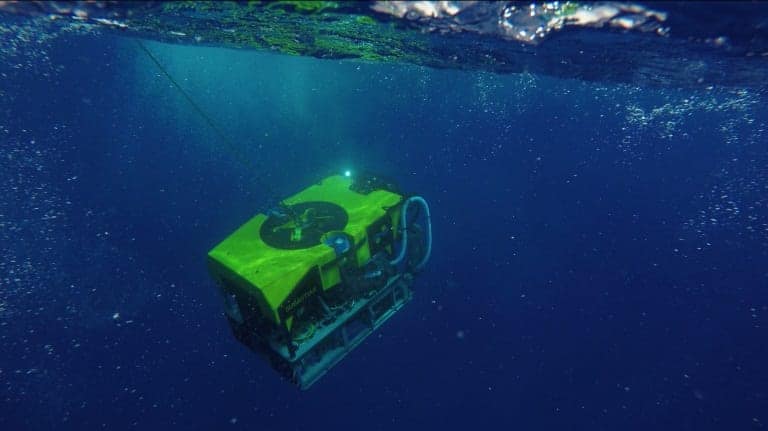
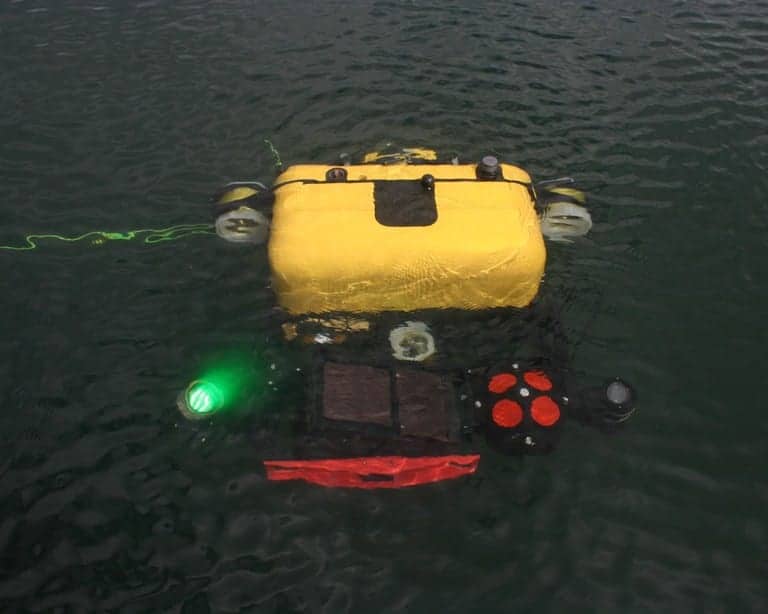
Riptide Autonomous Solutions, a developer of unmanned maritime vehicles, has announced that it has completed the delivery of its first three production Micro-UUVs to the US Navy’s SPAWAR Systems Center – Pacific. The unmanned undersea vehicles are configured with a flooded payload module that will enable rapid payload development and demonstration.
Riptide Autonomous Solutions, a developer of unmanned maritime vehicles, has announced that it has completed the delivery of its first three production Micro-UUVs to the US Navy’s SPAWAR Systems Center – Pacific. The unmanned undersea vehicles are configured with a flooded payload module that will enable rapid payload development and demonstration.
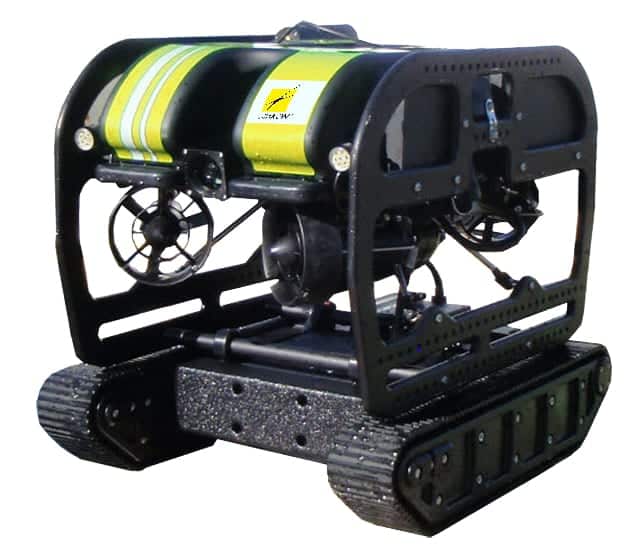
The Micro-UUV, Riptide’s first product, is a highly flexible, open source autonomous undersea vehicle that provides a state-of-the-art solution ideally suited for developers of autonomy and behaviors, power systems, subsea sensors, and new payloads. The Micro-UUV features open hardware and software interfaces, giving users a reliable and robust platform to advance technology development. The vehicle design is optimized for high efficiency and Riptide claims it has the best hydrodynamic signature in its class.
“This is an exciting milestone for Riptide. In less than one year’s time, we pulled together a great team of people and fielded a highly capable, highly flexible UUV at a very affordable cost point. The vehicle platform will continue to evolve and mature quickly, enabling end users to rapidly develop and demonstrate new applications in this growing market,” said Jeff Smith, Riptide’s President.
Riptide’s micro-UUV features three individually actuated control fins providing active roll stabilization. An active GPS antenna, WiFi communications, and vehicle recovery strobe LED’s are integrated into the vertical control fin, reducing the vehicle’s hydrodynamic signature for maximum efficiency. Multiple energy source options allow maximum flexibility for endurance, safety, shipping, and mission optimization. The Aluminum-Seawater Battery planned for demonstration in late 2016 from Riptide’s partner Open Water Power will provide unparalleled energy density (endurance) and safety.
The Micro-UUV features a flexible software architecture leveraging a large amount of open source software. Dr. Dani Goldberg, Riptide’s Software Principal, said: “It is our hope that an active and vibrant user community will grow around the Micro-UUV platform. To help foster this vision, we are providing users with Riptide-developed source code under a standard open source license. We are also maximizing our use of existing open source software, both to provide a mature platform and to tap into existing energetic user communities.” In the initial release of Micro-UUV software, Riptide is providing code for the Arduino and Beaglebone Black development platforms, as well as support for the MOOS-IvP robot control engine. Future releases are planned to include support for ROS (the Robot Operating System) and streamlined user interfaces.
The post Riptide Delivers Micro-UUVs to US Navy appeared first on Unmanned Systems Technology.